Three Way Handshake :
TCP/IP is the communication protocols used in connecting hosts between internet. Every OS in the market comes with the inbuilt TCP stack in them. Without the kernel's TCP network ,there is no possible data exchange can happen between devices, be it mobile devices, laptops, desktops and any other network hardwares.Among the 4 layers in the suite, the transport layer takes the responsibility of transmission,error detection,recovery,reliability and session control.
How does the data transmission really takes place?
The blocks of data are sent through the transport layer. Each segment of a message sent from the machine contains a checksum which checks if the data at the receivers's end is correct. If the data received at the destination is undamaged, then an acknowledgement will be sent to the sender machine, else the receiver discards the segment and the sender machine sends all the segments for which a positive acknowledgement has not been received.
This is the frame for a 3-Way HandShake. Three distinct segments are exchanged between the hosts for reliable TCP session to be established.
| EVENT | DIAGRAM |
Host A sends SYN to Host B
Host B receives A's SYN
Host B sends a acknowledgement SYN-ACK to Host A
Host A receives B's SYN
Host A sends a acknowledgement ACK to Host B
Host B receives A's ACK.
TCP socket connection is ESTABLISHED. | 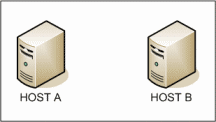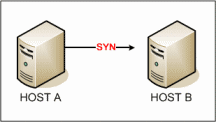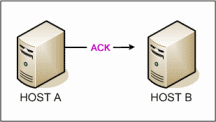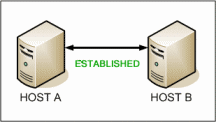 TCP Three Way Handshake (SYN,SYN-ACK,ACK) |
Steps in the handshake:
Machine A sends a SYN signal to initiate the connection to the target Machine B.
( 1 Shake)
SYN - synchronize sequence number . Its just the sequence number it starts the segment with.
Machine B acknowledges the communication with the SYN-ACK signal. It responds along with sequence number it will start with. (2 Shake)
Machine A, after receiving the acknowledgement from B, checks the SYN number from B and acknowledges the initial sequence number of B. A sends the final ACK signal and starts the data transferring in segments(bits). (3 Shake)
That's why this is called a 3 way Handshake (SYN - SYN - ACK)
TCP/IP is the de-facto standard for transmitting data over internet.


